With increasing approaches to transact and validate identification digitally, the requirement of keeping such data safe virtually is of paramount importance. Biometric devices are the very first type of solution which comes to mind when wanting to secure virtual data. These devices have not only evolved the process of identification to a high degree of accuracy but have also undergone development over time, enhancing security. In this blog, we will understand biometric devices, their uses and types.
What is Biometrics?
Biometrics refers to capturing or measuring, and analysing a human’s identifiable physical traits and behavioural characteristics. When such information is captured in any biometric device, it helps in validating the identity of any person. This can be done by acquiring relatable information like fingerprints, iris, voice, facial features, etc.
Importance of biometrics in modern identification and security systems
Modern identification and security systems refer to the digital setup which incorporates biometric devices or software. The following useful features make biometric devices a convenient option, proving their purpose of implementation in almost every sector.
- Enhance security: The process of maintaining records in physical register books is replaced with recording physical traits using biometric devices
- Convenience & speed: Passwords or physical cards were vulnerable to illegal hacking and theft. Such vulnerabilities are rare in biometric devices, as a mere face or fingerprint scan typically completes the identification.
- Security: Biometric devices are difficult to hack; hence, they help in keeping data safe, being one of the most trusted approaches to secure data
- Widespread application: Due to its enhanced features, biometric systems are used in almost every sector which requires keeping any sort of data safe. Voting booths, banking sectors, smartphones, and borderline security are some of the examples which heavily rely on biometric systems
Everyday uses: Smartphones, Banking, Aadhaar, etc.
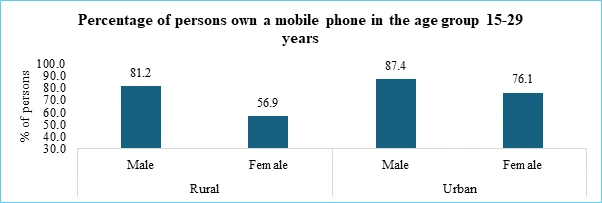
As per the Press Information Bureau’s release in May 2025, approximately 85.5% of households in India own at least one smartphone, and nearly 86.3% have internet connectivity within their homes. This high level of digital access reflects the growing online presence of individuals across various platforms. Most Indians are likely to have at least one account on popular social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and YouTube. Smartphones today are equipped with biometric features like fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, or iris scanning, which help secure sensitive data such as user IDs and passwords. These biometric systems are commonly used to unlock phones and enhance data protection.
Digital banking in India has expanded from urban cities to a significant portion of rural areas. Fintech companies like Biznext are enabling seamless and accessible digital transactions at every level. With services like money transfers, cash withdrawals, and loan applications just a few clicks away through smartphones or desktops, the need for secure digital platforms has become more critical than ever. Popular UPI-based apps such as Google Pay (GPay), PhonePe, and Paytm are widely used for day-to-day financial transactions. However, if the data used to access these services is compromised by cybercriminals, it could lead to severe financial losses that are difficult to recover. Hence, biometric authentication is now an integral part of most digital banking systems, offering an added layer of security.

Aadhaar, managed by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), is the world’s largest biometric identification system, covering over 1.3 billion individuals. It uses biometric data such as fingerprints, iris scans, and facial recognition, along with demographic information, to authenticate a person’s identity for various services like banking, subsidies, and digital transactions. To ensure the security of this massive database, UIDAI employs advanced encryption, multi-layered cybersecurity protocols, and regular audits. Access to Aadhaar data is tightly controlled, and biometric authentication is done in real-time through secure channels, making it both robust and privacy-conscious.
Biometric Meaning
Biometrics refers to the use of a person’s unique physical or behavioural features like fingerprints, face, eyes, or voice to identify and verify who they are. It’s a way to make sure that only the right person gets access to a phone, account, or service, using something that can’t easily be copied or stolen.

How biometrics identifies unique physical and behavioural traits
Biometrics capture physical and behavioural traits which cannot be duplicated or stolen, and more importantly, don’t change over time. The accuracy rate of biometrics is a maximum of 99.99% through iris scans, with a least of 80% – 90% by analysing gait. The following are examples of biometrics modalities.
- Fingerprint patterns – the ridges and loops on your fingers are unique, even between twins.
- Facial structure – the distance between your eyes, nose shape, and jawline are analyzed.
- Iris or retina scans – eye patterns are complex and stable throughout life.
- Hand geometry – shape, length, and width of fingers and palm.
- Voice recognition – based on pitch, tone, and speaking style.
- Typing rhythm – how fast and in what pattern you press keys.
- Gait analysis – how you walk, including posture and speed.
- Signature dynamics – not just what you write, but how you write it (pressure, speed, angle).
Biometric meaning in Hindi
बायोमेट्रिक का अर्थ है किसी व्यक्ति की पहचान उसके शरीर की विशिष्ट शारीरिक या व्यवहारिक विशेषताओं के आधार पर करना। इसमें उंगलियों के निशान (फिंगरप्रिंट), चेहरे की बनावट (फेस स्कैन), आंखों की पुतली (आईरिस स्कैन), आवाज़ की टोन, और चलने-फिरने की शैली (गेट एनालिसिस) जैसी खूबियों का उपयोग किया जाता है। ये विशेषताएं हर व्यक्ति में अलग होती हैं और समय के साथ ज़्यादा नहीं बदलतीं, इसलिए पहचान के लिए यह एक सुरक्षित और विश्वसनीय तरीका माना जाता है। आज के समय में मोबाइल फोन अनलॉक करने से लेकर आधार कार्ड आधारित पहचान तक, बायोमेट्रिक तकनीक का व्यापक उपयोग हो रहा है।
What Is a Biometric Device?
A biometric device is a type of equipment designed to capture and record unique biological data such as fingerprints, iris scans, or other biometric traits. These devices come in various forms, and the choice of device depends on the specific data an organisation or system needs to collect. For instance, workplaces often use fingerprint scanners, like those from Mantra, for attendance and access control. In Aadhaar card registration, both fingerprints and iris scans are required. In more serious scenarios, such as criminal investigations, forensic teams may use advanced biometric tools to analyse traits like gait patterns to help identify suspects.

The working of biometric devices follows a structured algorithm that captures the data, stores it and verifies its validity when required. The following process denotes the exact functioning of the biometric devices.
- Data Capture
The device uses sensors (optical, capacitive, or infrared) to scan a biometric trait, such as:
- A fingerprint scanner captures the ridge patterns on your finger.
- A facial recognition camera maps facial features and distances.
- An iris scanner detects the unique patterns in your eye.
- A voice recognition system records your speaking pattern.
- Feature Extraction
The device converts the captured image or signal into a digital format by extracting unique data points. These features (like fingerprint ridges or facial landmarks) are then processed into a biometric template using complex algorithms.
- Storage
The biometric template is securely stored. Importantly, this template is not a raw image, but a coded mathematical representation that cannot be easily reversed or faked.
- Locally (on a device, like a phone or card),
- Central database (e.g., Aadhaar system).
- Verification or Identification
There are two ways to verify identity:

- Verification (1:1 match): The system checks if the new scan matches a specific stored template. For example, unlocking your phone with your fingerprint.
- Identification (1:N match): The system searches the entire database to find the matching identity. For example, police identifying a suspect from a fingerprint database.
- Decision Making: Biometric system compares the live biometric input with stored data and generates a match score. If the score is above a defined threshold. Access is granted if the given information matches the stored information. If not, access is denied.
Advanced systems may also detect liveness to ensure the input is from a real person (not a photo, recording, or fake finger).
Types of Biometric Devices
- Biometric Fingerprint Scanner: It is widely used across India, for example, Aadhaar registration and verification. Such devices record the patterns of the fingerprint, which are unique and never-changing, hence assisting in identifying any individual.
- Iris Scanner: Used in high-security systems like UIDAI. It is also a convenient way to identify or verify any individual without having to touch the device.
- Face Recognition Devices: Yet another way to verify an individual with a touchless method. Merely by scanning the facial features, the verification is performed. However, in case of identical twins with maximum facial similarities, the face recognition devices can be easily tricked.
- Voice Recognition Devices: Such devices help in identifying any individual based on voice modulation, rate and type of speech, and accents. Devices like Alexa, personal devices integrated with such a biometric program, can recognise the authorised user.
Popular Biometric Device Brands in India
1.Mantra Biometric Devices:
Mantra Softech is a leading Indian manufacturer of biometric and security solutions, widely known for producing Aadhaar-compatible biometric devices. These devices are used in government schemes, banking services, eKYC processes, and attendance systems.
Features:
- High-speed fingerprint and iris capture
- STQC-certified (Standardisation Testing and Quality Certification from UIDAI)
- Plug-and-play USB interface
- Durable build with anti-scratch sensor surface
- Fast authentication and response time
- Supports RD (Registered Device) service for Aadhaar authentication
- L1 certification in advanced models for high-security compliance
Common models:
- MFS100 (Fingerprint Scanner L0): General eKYC, banking, attendance systems
- MFS110 (Fingerprint Scanner L1): Aadhaar services, DigiLocker, subsidy distribution
- MIS100 (Iris Scanner): Aadhaar registration and verification
- MFSTAB: Android-based Biometric Tablet used for field verification, mobile Aadhaar services
Compatibility with Aadhaar & banking systems
Mantra biometric devices are STQC certified and fully UIDAI compliant, making them highly compatible with various Aadhaar-enabled and digital banking services in India. These devices are widely used across sectors for secure identity verification and financial transactions.
Mantra devices support key Aadhaar-based operations such as:
- Aadhaar Authentication: Used for verifying identity through fingerprint or iris scans.
- eKYC (Electronic Know Your Customer): Seamless integration with UIDAI’s eKYC APIs for telecom, insurance, banking, and NBFCs.
- Aadhaar Enrollment & Updates: Devices like MIS100 (iris scanner) and MFS110 (fingerprint) are approved for biometric data capture during Aadhaar enrollment.
- Jeevan Pramaan: Digital Life Certificate authentication for pensioners using Aadhaar biometrics.
- L1 Certification: Devices like Mantra MFS110 meet UIDAI’s latest L1 biometric security standards, making them suitable for secure Aadhaar-based services.
Mantra devices are widely adopted in Indian banking and fintech systems, including:

- AePS (Aadhaar Enabled Payment System): Fingerprint authentication for balance inquiries, cash withdrawals, and money transfers.
- Micro-ATM Integration: Works with micro-ATMs for banking services in rural and remote areas.
- DBT (Direct Benefit Transfer): Used to authenticate beneficiaries and enable secure subsidy transfers.
- NPCI & UIDAI APIs: Compatible with National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) platforms and Aadhaar Authentication APIs.
- BC (Business Correspondent) Models: Mantra devices are ideal for banking agents conducting doorstep services using Aadhaar-based authentication.
2. L1 Biometric Device
L1 certification refers to a security standard defined by UIDAI (Unique Identification Authority of India) for biometric devices used in Aadhaar-based authentication. It ensures enhanced data protection and tamper-proof hardware. L1 biometric devices are mandatory for Aadhaar-based services because they meet higher security and compliance standards set by UIDAI to protect citizens’ biometric data.
- Enhanced Security at Hardware Level: L1 devices encrypt biometric data at the hardware level before it leaves the device. This means even if someone intercepts the data, it cannot be read or misused. In contrast, older L0 devices perform encryption at the software level, which is less secure and more vulnerable to tampering.
- Tamper-Proof Design: L1 devices are built with tamper-resistant technology. If anyone tries to physically alter the device or extract data, the device gets disabled. This protects against misuse and fraud.
- Compliance with UIDAI Guidelines: UIDAI, the authority behind Aadhaar, has made L1 devices mandatory since July 2022 for all Aadhaar authentication processes. This ensures all service providers, government or private, follow the same secure standards.
- Protection of Biometric Data: Aadhaar authentication involves sensitive biometric details like fingerprints and iris scans. L1 devices ensure this data is not stored or leaked and is securely transmitted through Registered Device (RD) services only.
Biometric Device Price in India
- General price range for fingerprint scanners varies depending upon company and version. The price ranges from ₹1,500 – ₹5,000
- L1 certified device price ranges from ₹3,000 – ₹8,000
- The price of Mantra MFS100 begins from ₹2949. Whereas the price of Morpho starts from ₹4500. Biometric device from Starteck can cost a minimum of ₹2800.
Factors affecting the price
The price of biometric devices varies due to their features, certifications and compatibilities.
- Certification: With UIDAI’s new guidelines discontinuing the use of L0 devices, all fingerprint scanners are now L1 certified. This shift has led to an increase in prices, as L1 devices come with certification that ensures compliance with all UIDAI regulations.
- Features: The price of biometric devices also depends on their features, such as the type of biometric scanning they support—fingerprint, iris, or facial recognition. Devices with more advanced or multiple scanning capabilities generally cost more.
- Compatibility: Biometric devices are expected to be compatible with multiple operating systems like Android, Windows, and Linux. The demand for broader compatibility and support for various SDKs (Software Development Kits) also contributes to higher pricing.
What Is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication refers to authenticating an individual based on his fingerprint scan, facial scan, iris scan or voice recognition. This is achieved by storing the scanned result in a virtual database, and the individual is authenticated every time he scans himself in any of the mentioned patterns. By authenticating an individual, the biometric device grants access, making it a secure and reliable method of authentication.
Difference between authentication and identification
Identification using biometrics refers to the process of determining a person’s identity by matching their biometric data against a database. In contrast, authentication is the process of confirming that an individual is indeed who they claim to be. While both processes are used to grant access to systems, services, or locations, they serve different purposes. Furthermore, modern biometric devices are equipped with advanced technology to detect and prevent fraudulent or deceptive attempts to gain unauthorised access.
Advantages of Biometric Devices: security, speed, and accuracy
With evolving and enhanced technologies, biometric devices are considered to be the most reliable devices as the data they capture by scanning physical features does not tend to change with time. Additionally, the following are the advantages of biometric devices.

- Security: Enhanced security system that detects impersonation or hacking attempts. For example, access is denied and the alarm is turned automatically if the biometric device detects any illegal attempt to access any service.
- Speed: Just by iris or facial scan, the authentication is done. No requirement of contacting anybody or seeking permission to grant or deny access.
- Accuracy: Biometric authentication shows 99.99% accuracy through iris and fingerprint scan. Facial scan and voice scan can give results with accuracy ranging from 80% – 90%
Benefits and Challenges of Biometric Devices
Benefits of Biometric Devices
- Increased Security
Biometric data such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial features is unique to each individual, making unauthorised access extremely difficult. This provides a stronger layer of security than traditional methods like passwords or PINs. - Fraud Prevention
Biometric authentication helps prevent identity fraud, impersonation, and unauthorised transactions—especially in critical areas like banking, Aadhaar-based services, and public distribution systems. - User Convenience
Users don’t need to remember passwords or carry ID cards. A simple fingerprint or face scan enables fast and seamless access to services, devices, or secure locations.
Challenges of Biometric Devices
- Privacy Concerns
Biometric data is highly sensitive. If misused or compromised, it can’t be changed like a password. This raises serious concerns about data security, storage, and misuse by unauthorised entities. - Device Accuracy Issues
Biometric devices may occasionally fail to authenticate users due to poor fingerprint quality, dirt, injuries, ageing skin, or environmental conditions, causing inconvenience or access denial. - Cost of Certified Devices
L1-certified biometric devices (mandated for Aadhaar-based services) are expensive due to the added hardware encryption, compliance standards, and RD (Registered Device) certification, making them less accessible for small businesses or individuals.
Future of Biometrics in India
India is globally recognised for its pace toward digitisation. From social media to online banking, India has shown an exponential surge in building its digital presence. And for every online access, Indians heavily rely on biometrics as it promises a safe and secure gain of online access. Biometrics is getting implemented not just in technological gadgets, software applications, and offices but also at household entrances.
Fintech companies like Biznext, dedicated to advancing financial inclusion in rural India, prioritise service quality and reliability. They understand the importance of using high-quality biometric devices, especially for critical financial services such as AEPS, money transfers, and cash withdrawals. These transactions demand devices that are not only secure but also durable and efficient. That’s why Biznext strongly advocates for the use of L1-certified biometric devices, which offer enhanced security and compliance with regulatory standards.
Government Schemes That Use Biometric Authentication
- Aadhaar-Enabled Public Distribution System (AePDS):
Biometric fingerprint scan is used to verify beneficiaries before providing subsidised ration, helping eliminate fake or duplicate entries. - Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT):
Aadhaar-linked biometric verification ensures that government subsidies (like LPG, pensions, and welfare schemes) are transferred directly to the rightful beneficiaries. - MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act):
Biometric-based attendance and Aadhaar-linked bank transfers ensure accurate wage payments and reduce ghost workers. - Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY):
Biometric KYC is used for account opening, and AEPS (Aadhaar Enabled Payment System) allows people to perform banking transactions using just a fingerprint. - Ayushman Bharat – PM-JAY:
Patients are verified through biometrics at hospitals to confirm their identity before receiving free treatment under the scheme. - Digital Life Certificate (Jeevan Pramaan):
Pensioners use biometric authentication to submit their life certificates digitally, avoiding the need to visit pension offices in person. - e-KYC for Mobile SIM Activation:
Telecom companies use biometric fingerprint or iris scans for Aadhaar-based eKYC to issue new SIM cards securely. - Scholarship Schemes:
Students are authenticated using Aadhaar biometrics to avoid duplication and ensure that scholarships reach the intended recipients. - Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS):
Allows banking transactions like withdrawals and deposits through micro-ATMs using Aadhaar number and fingerprint, especially in rural areas.
Upcoming trends: multimodal biometrics, AI-integrated systems
Multimodal biometrics: Biometric devices are constantly developed in order to improve their performance with every new version. Multimodal biometrics are devices that can scan multiple physical traits instead of any single trait. For example, such devices are already implemented in places like offices and hospitals, which easily authenticate employees through fingerprint or facial scans. Following are the features of multimodal biometrics:
- Higher accuracy
- Improved security
- Reduced chances of spoofing or errors
AI-integrated systems: Artificial Intelligence has boosted the efficiency of biometric devices through its modern technologies. With AI, biometric devices can easily track malicious attempts of gaining access to restricted services. AI algorithms in biometric devices help in:
- Real-time facial recognition
- Adaptive learning from new biometric data
- Detecting spoofing attempts or deepfakes
- Faster and more accurate matching in large databases
Conclusion
Biometrics involves using unique physical traits for identity verification and plays a vital role in ensuring secure, fast, and fraud-resistant access across various sectors. Choosing the right biometric device depends on the specific needs of the organisation or business where it is being implemented. For official purposes, especially Aadhaar-based services, L1-certified devices are mandatory as they provide enhanced security, encrypted data handling, and full compliance with UIDAI guidelines.
FAQs on biometric devices
- What is the difference between L0 and L1 biometric devices?
Answer: L0 device was the first version of biometric devices whose sole purpose was mass enrollment of Aadhar cardholders. L1 device is the advanced version, which is comparatively more reliable and secure than L0.

- Which biometric device is best for Aadhaar authentication?
Answer: For most common Aadhaar-based services like AEPS, eKYC, DBT, fingerprint scanners like Mantra MFS100 L1 or Startek FM220U L1 are the most cost-effective and widely accepted options. - How much does a Mantra fingerprint scanner cost?
Answer: The price of a Mantra L1-certified fingerprint scanner, such as the MFS110, typically ranges from ₹2,990 to ₹3,799, depending on the vendor and whether RD service is included. - Can I use biometric authentication on my phone?
Answer: Yes, one can use biometric authentication on a phone, as most of the phones have biometrics already integrated in themselves.
Also read: Aadhaar self service update portal (SSUP UIDAI)