Digital payments in India refer to electronic transactions made through various platforms like mobile wallets, online banking, and UPI (Unified Payments Interface). This system allows users to send and receive money instantly using their smartphones or computers, making transactions faster and more convenient.
India’s digital payment landscape has changed dramatically in recent years, especially after two major events: The Demonetization in 2016 and The COVID-19 pandemic.
The Demonetization movement started by our Prime Minister aimed to reduce black money by removing certain currency notes from circulation. This sudden change forced people to find new ways to pay for goods and services.
Digital payments, such as mobile wallets and online banking, gained popularity as people looked for quick and safe alternatives. Apps like Paytm, Google Pay, and PhonePe saw a huge increase in users, making digital transactions more common in everyday life and giving a boost to India to go digital.
Then, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the need for contactless payment options surged. With social distancing measures in place, many people preferred to avoid cash transactions. This led to a further rise in digital payments, as more businesses adopted online payment methods. The convenience of paying through mobile phones helped people feel safer while shopping and paying bills.

The total number of digital payment transactions in India increased from 2,071 crore in 2017-18 to 18,737 crore in 2023-24. UPI transactions have grown from 92 crore in 2017-18 to 13,116 crore in 2023-24.
As more people adopt digital payments, ensuring their security is vital for maintaining confidence in this growing digital economy. Safe and reliable payment systems will help India move toward a more cashless future.
What is a Digital Fraud?
Digital payment fraud includes any form of dishonest or illegal activity carried out via the Internet. Typically, it means tricking people or organizations with technology in order to steal money, information, or personal information. As more individuals and companies utilize the Internet for communication, shopping, and banking, digital fraud is becoming a significant problem.
Online payment fraud can occur using electronic devices such as computers and smartphones or on the Internet. Emails, websites, social media, and mobile apps all fall under this category. Con artists trick others into thinking things that are untrue. To win people over, they frequently fabricate identities or situations. Let’s examine the various forms of digital payment fraud in India.
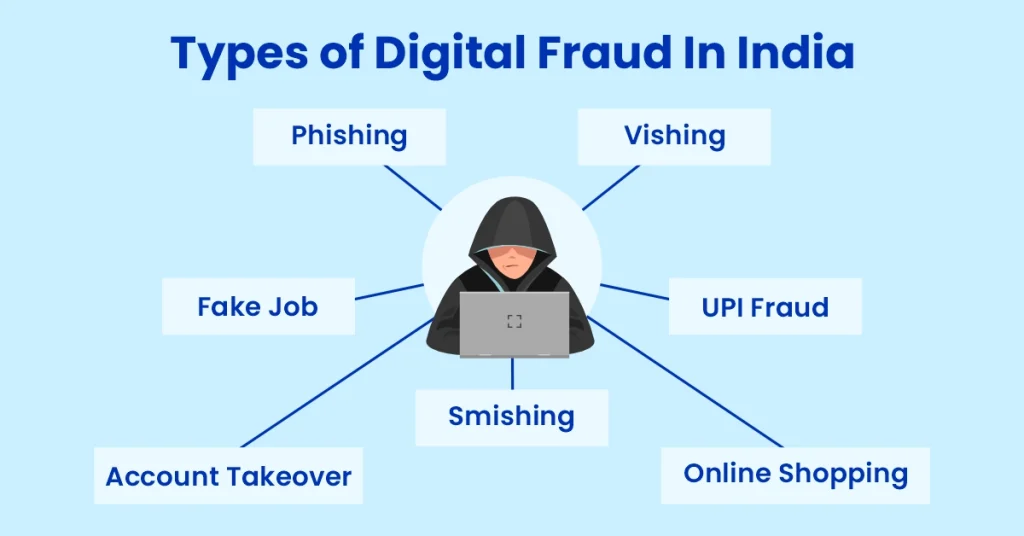
Types of Digital Fraud in India
Phishing
Phishing is an internet fraud that is one of the main issues that banks around the world struggle with. Hackers attempt to obtain the data by sending an email that appears to be from a trustworthy source, such as a bank or institution.

When you click on the action link in these emails, you will be taken to their webpage where you can access your personal data. Smishing is a similar tactic used via text messaging, whereas vishing is done over the phone.
Vishing (Voice Phishing)
Vishing is a type of phishing conducted over the phone. Scammers call victims, pretending to be from a bank or government agency, and ask for sensitive information. A caller might claim there’s a problem with your account and request your PIN or other personal details. Once they have this information, they can access your accounts.
Smishing (SMS Phishing)
Phishing and smishing are similar, however smishing occurs via SMS (text messages). Scammers frequently ask for personal information in their messages or provide links to fake websites. For instance, a message may inform you that you have won something and that you must click on a link to claim it. This link will take you to a false website that requests personal information.
Online Shopping Fraud
When customers purchase goods from fake internet retailers, fraud of this kind takes place. Fraudsters build websites that appear authentic, offer things at discounted rates, and then withdraw funds without fulfilling the orders. For example, after making a purchase, someone might order a smartphone from a website that isn’t real.
Account Takeover
In account takeover fraud, scammers gain access to a person’s online accounts (like email, bank accounts or social media) and misuse them. This can happen through phishing or data breaches.

Once they access the account, they can change passwords, steal money, or impersonate the victim to scam others. If a hacker accesses your email or social media they might request money from your contacts pretending to be you.
Fake Job Scams
In these schemes, fraudsters create job postings and demand payment for training materials or application fees from potential candidates. For example, a victim may apply for a job, be required to pay a fee for a background check, and then discover that the position was fraudulent.
Know 17 Common Job Scams
UPI fraud
Using a UPI app, the fraudsters deposit money into the victim’s account and then contacts the victim to demand payment. If the victim repays through the UPI app, the software infects their device giving them full access to their bank data. We refer to this as a UPI scam or UPI payment fraud.
Awareness is key to avoiding these scams. Always verify the source of messages or calls, avoid sharing personal information, and be cautious when clicking links or making online purchases.

Notable Digital Fraud Incidents in India
With millions of victims and huge financial losses, digital payment fraud has become a serious menace in today’s technologically advanced society. Fraudsters are creating more complicated schemes to trick innocent consumers as online transactions grow more widespread. In order to demonstrate the consequences of online payment fraud and the urgent need for payment fraud risks and preventive measures, this case study examines major cases of the crime.
Case Study: Chinese Loan Apps Scam in India
In 2020, India faced a major issue with illegal Chinese loan apps. These apps offered quick loans with very little paperwork, attracting many people in need of money. Reports indicated that over 10 million individuals had fallen victim to these scams. Once borrowers accepted the loans, they were hit with extremely high interest rates and hidden fees. If they struggled to repay, the apps used harsh tactics, like threatening to share personal details with family or employers.
This led to a cycle of debt for many victims, with some even taking extreme measures due to the pressure. While efforts have been made to curb the Chinese loan apps scam in India, it has not been entirely stopped. Authorities, including the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and law enforcement agencies, have taken action against many illegal lending platforms. They have blocked numerous apps, arrested several individuals involved in these operations, and implemented stricter regulations for digital lending.
However, new fraudulent apps continue to emerge, often adapting quickly to evade detection. The challenge remains in monitoring and regulating the vast number of digital financial services. Continued awareness campaigns and legal actions are essential to protect consumers and reduce the prevalence of these scams. Despite progress, the threat of such predatory lending practices persists, necessitating ongoing vigilance from both authorities and the public.
Case Study: Jubilant FoodWorks Data Breach
The parent company of Domino’s India, Jubilant FoodWorks, experienced a serious data breach in 2021 that resulted in the exposure of private client data. An estimated 18 crore usernames, email addresses, and phone numbers were allegedly acquired by a hacker. The hack was concerning since it brought up issues with major corporations data security and privacy.

Customers were alarmed about possible identity theft when the hacker allegedly demanded a ransom to stop the stolen data from being posted online. In response, Jubilant FoodWorks indicated that the breach did not involve financial data, but the event showed gaps in their cybersecurity efforts.
This case highlighted the need for tougher data protection rules and reinforced the need of solid security policies for organisations handling sensitive consumer information. Protecting consumer data continues to be a top concern for businesses in a variety of industries as digital threats continue to change.
Case Study: SIM Card Swapping Scams
SIM card swapping scams have become a growing concern in India, with thousands of individuals falling victim. In this scam, fraudsters manipulate mobile service providers to take control of a victim’s phone number. Reports suggest that over 5,000 cases were reported in just one year, resulting in millions of rupees lost.
The scammers often gather personal information through phishing calls or social media, pretending to be the victim to request a new SIM card. Once they gain access, they can reset passwords for banking and other accounts, leading to unauthorized transactions. Many victims have reported losing significant amounts, with some cases involving losses exceeding ₹10 lakh.
To combat this issue, authorities have increased awareness campaigns and urged mobile service providers to enhance verification processes. This case highlights the urgent need for consumers to safeguard their personal information and for telecom companies to strengthen their security measures against such fraudulent activities.

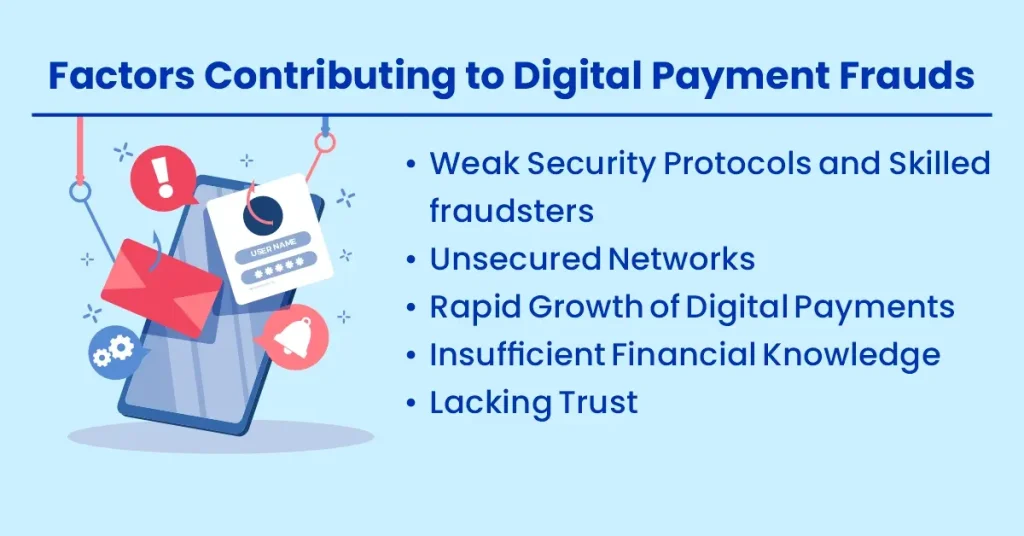
Factors Contributing to Digital Payment Frauds
Weak Security Protocols and Skilled fraudsters
A lot of companies and people fail to put strong safety measures in place, such as enabling two-factor authentication and creating secure passwords. Simultaneously, fraudsters are constantly improving their techniques and using modern technology.
This combination makes the atmosphere unsafe. It is simpler for fraudsters to gain access to accounts and steal money or personal data when security measures are lacking. These thieves are getting more crafty and have new tricks up their sleeves that can fool even highly technological individuals.
This implies that common people and businesses have difficulty identifying fraud, which increases the likelihood of successful fraud efforts and financial losses.
Unsecured Networks
Nowadays, people often connect to public wifi networks or any open wifi network that is available in order to conserve their mobile data or because they are in the habit of constantly accessing the internet. Since public Wi-Fi networks might not be safe, using them puts consumers at risk. Payment information can be stolen by hackers thanks to their ability to intercept data sent across unsecured networks.
Rapid Growth of Digital Payments
With the increasing worldwide acceptance of digital payments, more individuals and companies are utilizing technology to streamline and accelerate transactions. Online banking services, smartphone wallets, and new payment platforms have all been made possible by this explosive growth.

But as these systems develop, scammers quickly modify their strategies to take advantage of holes in these new technologies. When new payment methods are launched, they might not have been adequately verified for security issues, leaving loopholes that fraudsters might exploit.
Furthermore, in their haste to embrace new technology, companies and customers could neglect essential security precautions like appropriate encryption or authentication. Fraudsters can create new attack strategies as they research these developing systems.
This constant game of catch-up between security measures and fraud tactics means that while digital payments offer convenience, they can also create an environment ripe for fraud, leading to financial losses and diminished trust in digital payment systems.
Insufficient Financial Knowledge
It’s possible that a lot of individuals, particularly in India, are unaware of financial goods or the operation of digital payments. People are more susceptible to scams as a result of their ignorance. They could fall for fraud because they are unable to spot warning signs in dubious emails or offers.
Lacking Trust
Because they are afraid of falling victim to online fraud, a lot of people could be skeptical or suspicious of using digital payments.

People’s options for safe transactions may be limited if they are reluctant to use digital payment methods due to this lack of trust. It can also lead to hesitancy in disclosing information, which is important for safer transactions.
Government and Regulatory Initiatives to Combat Frauds
Adoption of Advanced Technologies and Digital Payments Intelligence Platform
In order to effectively prevent payment fraud risks, governments are increasingly utilizing cutting-edge technology like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Real-time analysis of transaction patterns is made possible by these technologies, which aid in spotting suspicious activity and stopping fraud before it starts.
To boost these efforts, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is creating a Digital Payments Intelligence Platform aimed to promote real-time data sharing across the digital payments ecosystem. In the end, this platform will increase customer confidence in digital transactions by improving fraud detection capabilities and reducing risks.
Payment System Standardization
There is a push to standardize digital payment methods and protocols in order to improve security and guarantee compatibility across various platforms. Strong security measures are easy to implement as a result of this standardization.
Furthermore, by virtue of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act, 2023) all digital data must be gathered with the consent of the user and used exclusively for the purposes specified. When taken as a whole, these projects seek to make the digital payment landscape more open and safe, safeguarding user data and enabling safe cross-platform transactions.

Fraud Reporting Mechanisms
Governments are establishing platforms for consumers to easily report fraud incidents, enhancing the response to such issues. One such platform is the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP), which allows users to report cybercrime complaints, including online financial fraud. Complaints can also be filed by calling the National Cyber Crime Helpline at 1930.
This streamlined reporting helps authorities gather data on fraud patterns, leading to quicker investigations and more effective fraud prevention strategies. By facilitating easy reporting, the NCRP plays a vital role in improving the overall response to cybercrime and protecting consumers.
Best Practices for Users to Avoid Digital Payment Frauds
Maintaining financial security and protecting against illegal transactions can be achieved by being aware of the latest techniques for fraud prevention. People can profit from digital payments with more peace of mind by taking preventive measures such as:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
By requiring multiple forms of authentication in order to access an account, MFA offers an additional layer of security. For instance, you might be required to enter a code received on your phone after entering your password. Even if someone knows your password, this makes it far more difficult for them to access your account.
Maintain APP/Software Updates:
Updating your apps and software on a regular basis guarantees that you have access to the most recent security features and patches for any identified flaws. Outdated software is a common target for cybercriminals, so staying up to date helps shield you from such dangers.

Secure Networks:
Whenever possible, connect to private, secure networks, especially while transacting online. Because hackers can readily intercept your data, using public Wi-Fi might be unsafe. For increased protection, think about utilizing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) if you must utilize a public network.
Transaction Monitoring:
Keep a close eye on all of your financial transactions to look for any strange or unauthorized activity. Real-time transaction alerts are provided by many banks and payment providers, which make it easier for you to spot and report any suspicious activity right away. By being proactive, fraud can be detected before it gets worse.
Implement Machine Learning Algorithms:
Fraud detection systems can discover odd trends in transactions by utilizing machine learning. Large volumes of data may be analyzed by these algorithms, which allow for faster reactions to possible fraud by identifying irregularities that a human might overlook. This technology can increase security by adjusting to new threats as they emerge.
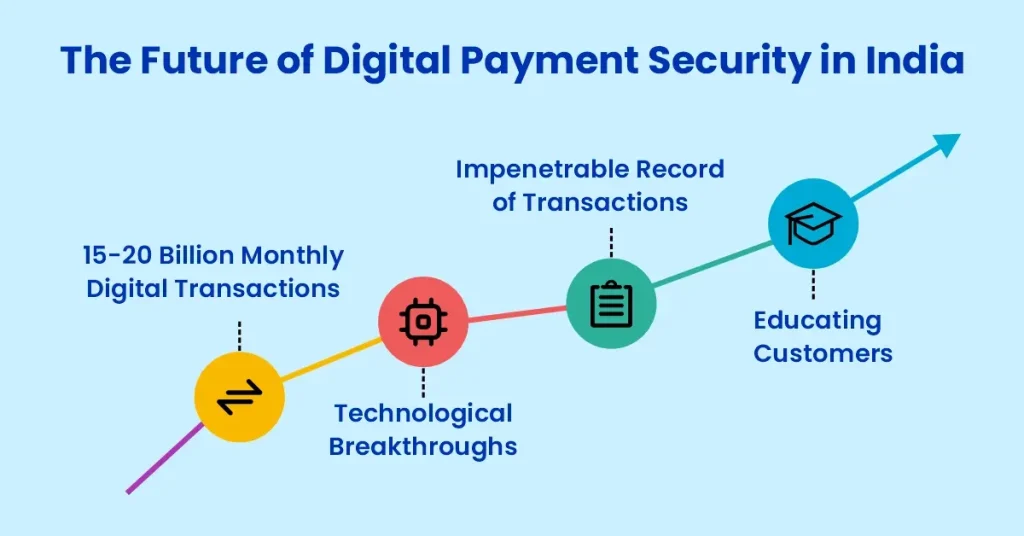
The Future of Digital Payment Security in India
The NPCI, which was founded as an effort by the RBI and the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) with a goal of 15-20 billion monthly digital transactions by volume, is expected to dominate the nation’s payments system. By the end of 2024, it is predicted to have facilitated more than half of all digital payments in India but with increasing transactions comes increasing risks.
Thanks to technological breakthroughs, digital payment security in India has a promising future. When compared to standard passwords, enhanced authentication techniques like fingerprint and facial recognition will offer higher security. Real-time analysis of transaction patterns by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will aid in the detection and prevention of fraud.

By offering an impenetrable record of transactions, blockchain technology can improve security and transparency. Stricter regulations are also anticipated to be introduced by the Indian government and regulatory agencies in order to safeguard customers and guarantee the security of digital payments. Ultimately, educating customers about safe online behavior will be essential to control payment fraud risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, major occurrences like the pandemic and demonetization have contributed significantly to the quick evolution of India’s digital payment system. Transactions have become easier as a result, but there is now a greater chance of fraud and fraud online. Many people become victims of dishonest acts, which emphasizes the importance of raising awareness and exercising caution.
Authorities are taking steps to tighten protections and promote safer online environments. By forming wise habits, users can improve their security. It will be crucial to put safety first as the digital economy grows in order to promote more adoption and trust in these payment options.
Read more- Digital Payments in India